tncRNA Toolkit
| 1. Brief Introduction | 2. tncRNA Toolkit workflow |
| 3. Download | 4. Prerequisites |
| 5. Installation | 6. Inside the Package |
| 7. Usage | 8. Output |
1. Brief Introduction
tncRNA Toolkit is designed for the identification of tRNA-derived small ncRNAs (tncRNAs) from high throughput sequencing data. This is built in the python3, alongwith shell/bash programming language. It can detect tncRNAs generating from either mature tRNAs or their leader or trailer sequences (upto 50 bp) viz. tRF-5, tRF-3(CCA), tRF-1, leader tRFs, 5’ tRH, 3’ tRH(CCA) and other-tRFs depending upon their site of cleavage on their parental tRNAs and length.
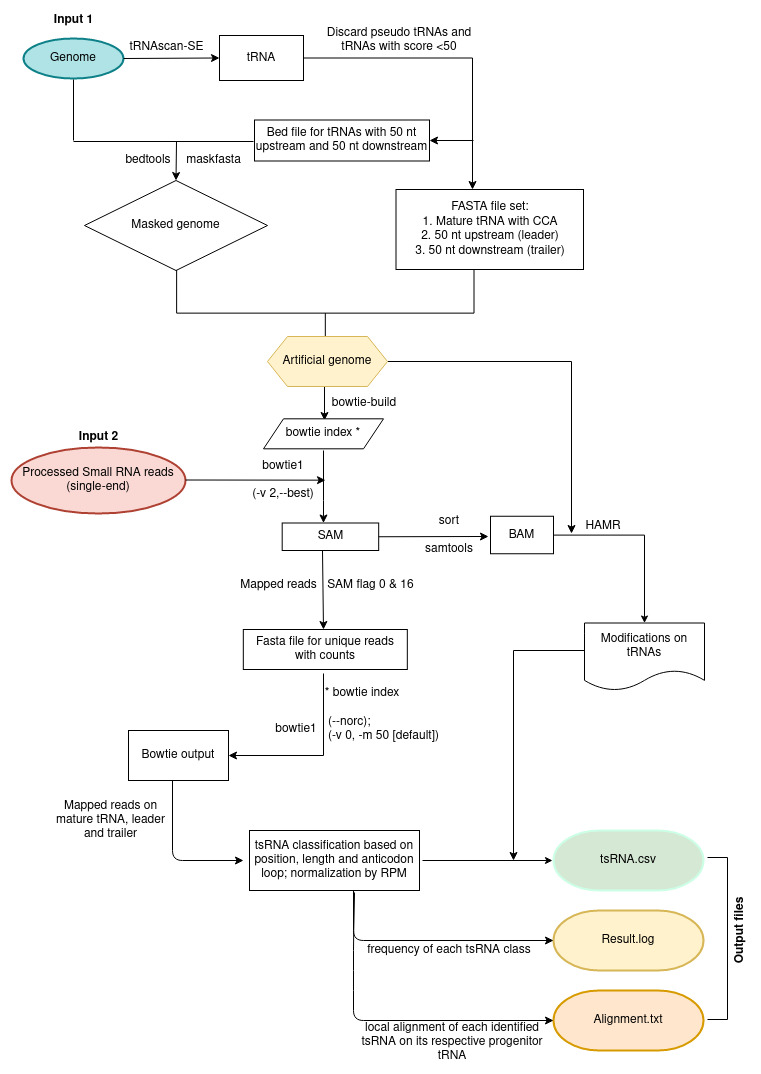
2. tncRNA Toolkit workflow
3. Download
Download the tncRNA Toolkit package from below link:
tncRNA-Toolkit.tar.gz
Note: This pipeline is tested on CentOS 7/8.
4. Prerequisites
1. python3
Python modules: pandas (v1.1.0), biopython (v1.77)
Python module can be easily installed by following command:
pip3 install <module name> --user
2. tRNAscan-SE (v2.0.6)
3. samtools (v1.10)
4. bedtools (v2.29.2)
[Note: python3, tRNAscan-SE, samtools, and bedtools are needed to be globaly installed or included it in the path.]
5. Bowtie1 (v1.3.0)
6. HAMR (v1.2)
[Note: bowtie1, and HAMR are already provided in tar package.]
5. Installation
Extract the tarball using the command:
tar -xf tncRNA-Toolkit.tar.gzcd tncRNA-Toolkit/Installing bowtie1:
cd util/unzip bowtie-1.3.0-src.zipcd bowtie-1.3.0-src/makecd ../../[Note: HAMR-1.2 is already extraced in 'util/HAMR-1.2' and it required python2 for running. If you have python2, then no need of further installation for HAMR.
6. Inside the Package
This distribution includes the python3 script tncRNAs.py and other scripts in the ‘util’ folder which are needed to run the main script.
7. Usage
First, create bowtie index for genome:
python3 tncRNAs.py -g <genome fasta> -s <species name>It will automatically create the bowtie index alongwith needed files in "lib/indexes/<provided species name>"
Note:
Genome fasta header should start with '>chr[Num]'. Mitochondrial and plastid fasta headers also should be as chrMt & chrPt respectively. This will be helpful for automation of scripts, and separation of nuclear & organellar region.
Once dealt with index build, user can further analyse the processed sRNA single-end data for that species.
tncRNAs prediction:
python3 tncRNAs.py -s <species name> -i <processed small RNA reads> -o <output dir>
Options-
-h print help
-s species name
-i small RNA reads (quality filtered and adapter trimmed)
fastq (.fastq/.fq) file
-o output directory
Miscellaneous options-
-v <int> mismatch or gap allowed [default: 0]
This option is for providing the integer value for -v option to the Bowtie aligner. It is recommended not to provide value >3.
-m <int> limit to suppress all alignments if more than
-c <int> cut-off value for read count [default: 10]
-t <int> number of threads [default: 1]
8. Output
In the provided directory with ‘-o’ option, tncRNA Toolkit provides three result files:
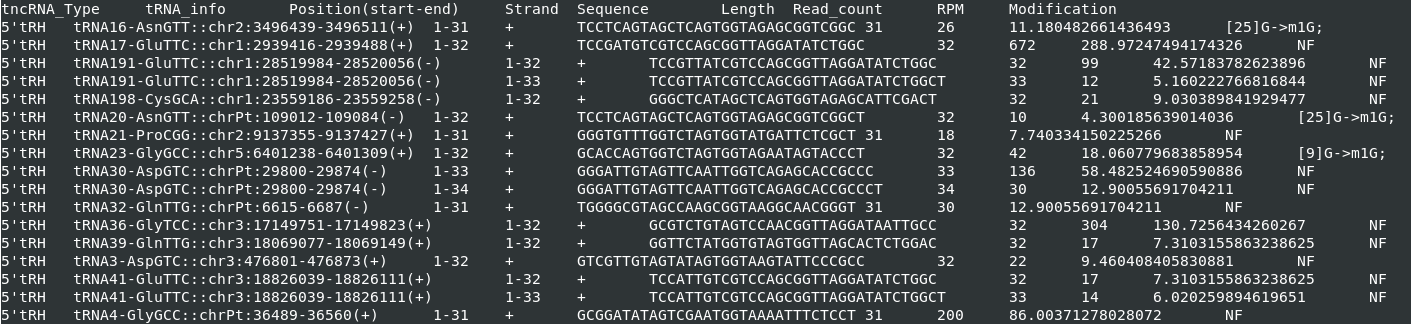
1. tncRNAs.csv
tncRNAs findings and their respective parental tRNA information, strand, sequence, length, read count, RPM value and Modification are stored in tncRNAs.csv.
Total of nine columns in tncRNAs.csv (shown in Figure 3) are as follows:
1. tncRNA_Type:
Different type of tncRNAs: tRF-5', tRF-3'(CCA), 3’ tRH(CCA), 5’ tRH, tRF-1, leader-tRF and other-tRF.
2. tRNA_info:
This column contains tRNA information in the following format:
tRNA:amino_acid:anticodon::chromosome:start-end(strand)
'ld_tRNA' means the leader sequence of the corresponding tRNA.
It is 50 bp upstream to the chromosome locus of respective tRNA.
While, 'tl_tRNA' is the trailer sequence, 50 bp downstream to tRNA sequence.
3. Position(start-end):
This is the aligned-position of tncRNA on its respective origin
(mature tRNA, trailer or leader sequence).
4. Strand:
The +ve/-ve strand of tRNA origin, on which tncRNAs are aligned.
5. Sequence: tncRNA sequence
6. Length: Length of tncRNA
7. Read_count:
Total number of mapped reads from small RNA-Seq supporting the tncRNA.
8. RPM: Reads per million
9. Modification: [base position on tRNA]base->Modification
"NF" in column, if no modification found for tncRNAs.
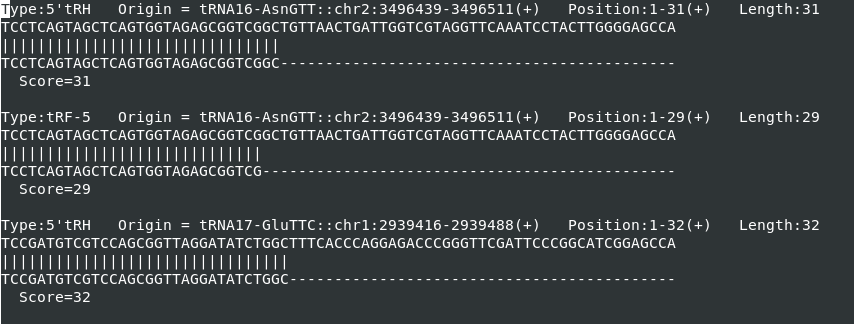
2. Alignment.txt
This file depicts the alignment of each tncRNA sequence over
its origin sequences, i.e., mature tRNA, 5’ leader and 3’ trailer precursor
tRNA sequences, including basic meta-information from tncRNAs.csv (Figure 4).
Scoring is provided as per parameters:
identical=1, non-Identical=-1, gap-open=-1, gap-extend=-0.5
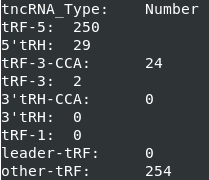
3. Result.log
The statistical information regarding the total count of different tncRNA sub-types are stored by this log file (Figure 5).
Note: ‘tncRNAs.csv’ and ‘Alignment.txt’ files will not be generated if no tncRNAs are detected in a sample!
