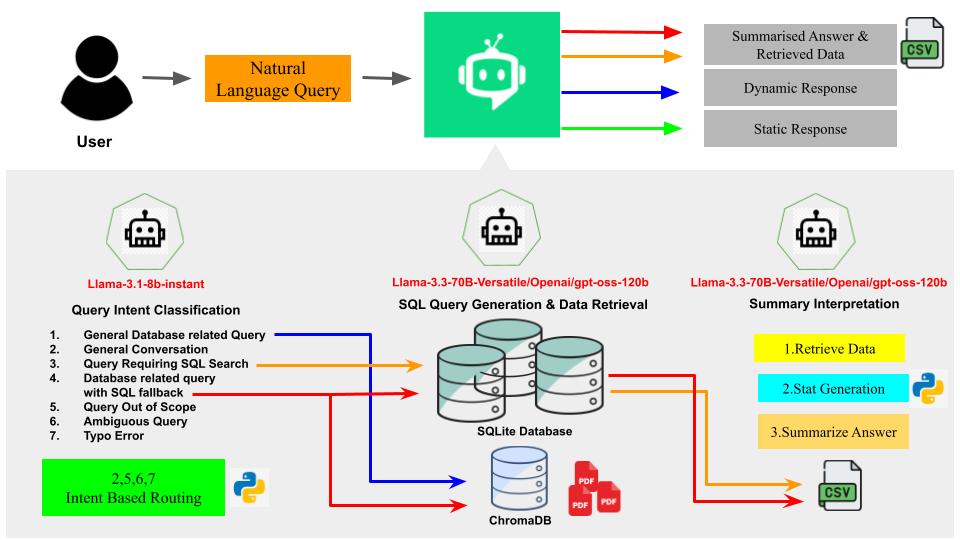
Every query is processed through an orchestrated workflow to ensure accuracy and relevance, transforming your question into a clear, data-backed answer.
1. Intent Classification
First, your query is classified to determine its intent (e.g., data retrieval, metadata question, or general conversation). This allows the system to choose the most efficient path—either querying the database, consulting our knowledge base via RAG, or providing a direct conversational reply.
2. SQL Query Planning
For data-related questions, the powerful LLM, guided by the database schema and a curated knowledge graph, translates your natural language query into one or more precise, executable SQL statements. This plan ensures the correct tables and columns are queried.
3. Data Retrieval & Processing
The generated SQL queries are safely executed on read-only copies of our SQLite databases. The raw data is then processed using pandas to compute statistical summaries and prepare it for interpretation, with large datasets being intelligently sampled for efficiency.
4. Summary Generation
Finally, the LLM transforms the structured data and statistical reports into a coherent, easy-to-understand conversational summary. The final response, along with a link to download the full dataset as a CSV, is delivered to you in a clean JSON format.